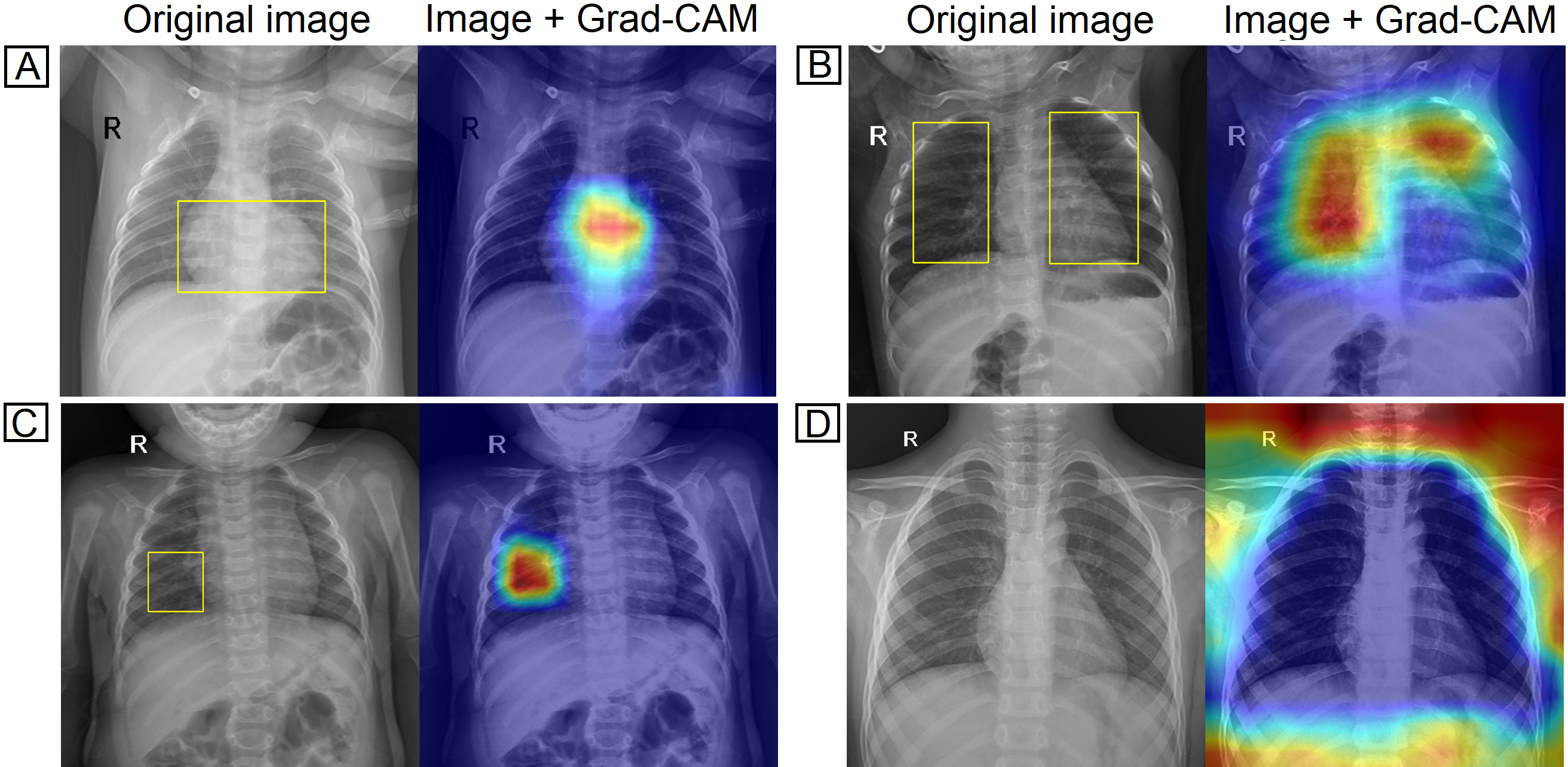
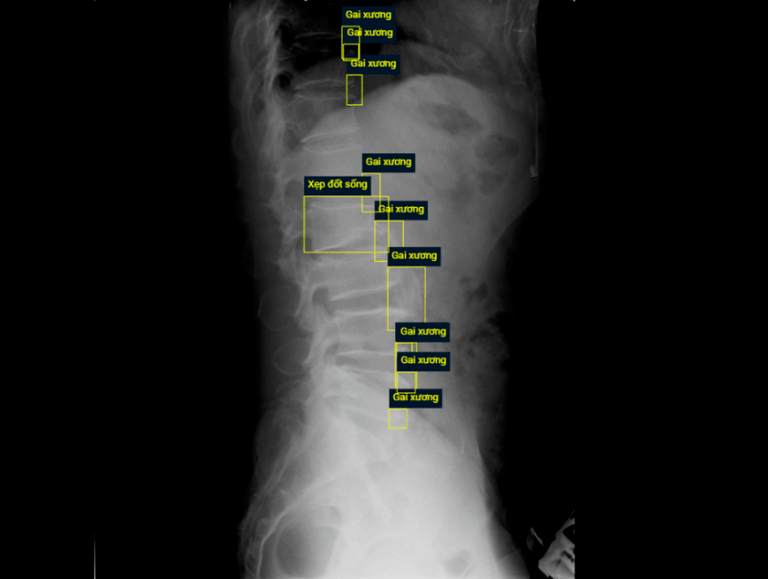
Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems for chest radiographs using artificial intelligence (AI) have recently shown a great potential as a second opinion for radiologists. The performances of such systems, however, were mostly evaluated on a fixed dataset in a retrospective manner and, thus, far from the real performances in clinical practice. In this work, we demonstrate a mechanism for validating an AI-based
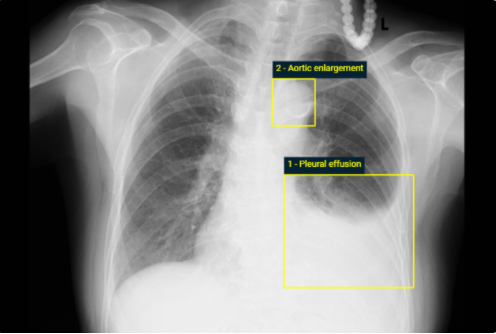
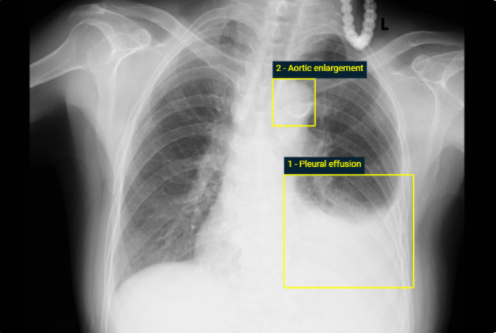
system for detecting abnormalities on X-ray scans, VinDr-CXR, at the Phu Tho General Hospital–a provincial hospital in the North of Vietnam. The AI system was directly integrated into the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) of the hospital after being trained on a fixed annotated dataset from other sources. The performance of the system was prospectively measured by matching and comparing the AI results with the radiology reports of 6,285 chest X-ray examinations extracted from
the Hospital Information System (HIS) over the last two months of 2020. The normal/abnormal status of a radiology report was determined by a set of rules and served as the ground truth. Our system achieves an F1 score–the harmonic average of the recall and the precision–of 0.653 (95% CI 0.635, 0.671) for detecting any abnormalities on chest X-rays. Despite a significant drop from the in-lab performance, this result establishes a high level of confidence in applying such a system in real-life situations.
A clinical validation of VinDr-CXR, an AI system for detecting abnormal chest radiographs